Ch103 – chapter 8: homeostasis and cellular function – chemistry Homeostasis body maintain human work do why important internal environment temperature stimulus condition sweat Anatomy&phys: homeostasis
What Is Homeostasis? » ScienceABC
Homeostasis homeostatic control temperature feedback body mechanisms controls anatomy negative diagram blood hypothalamus cold external factors when regulation affect thermoregulation
Homeostasis: positive/ negative feedback mechanisms : anatomy & physiology
6biopinos: homeostasisFeedback homeostasis positive mechanisms homeostatic maintain physiology anatomy regulation effector stimulus interactions Homeostasis feedback mechanisms biology definition negative loop ls1 illustration organism[ls1-3] feedback mechanisms and homeostasis.
Homeostasis calcium other body systems skeletal maintain organ interactions system role kidney mechanism do calcitonin work blood activity too figureHomeostasis cellular function feedback temperature chemistry regulation homeostatic positive fever humans ch103 core 😀 why is homeostasis important for the body. why is homeostasisFeedback homeostasis negative body positive system human mechanisms control homeostatic anatomy physiology maintain systems definition biology receptor loop diagram cell.

Homeostasis humans
What is homeostasis? why is it so important for our wellbeing?Homeostasis types pressure applications hypothalamus maintain physiology anatomy normal microbenotes cortisol functioning brain nervous organs What is homeostasis? » scienceabcHomeostasis definition maintaining mechanism flow byju meaning ecosystem negative definitions byjus endocrine external.
6.7 calcium homeostasis: interactions of the skeletal system and otherHomeostasis blood vessels regulation heat nervous glands secrete shivering causes constrict dilate Maintaining homeostasis.






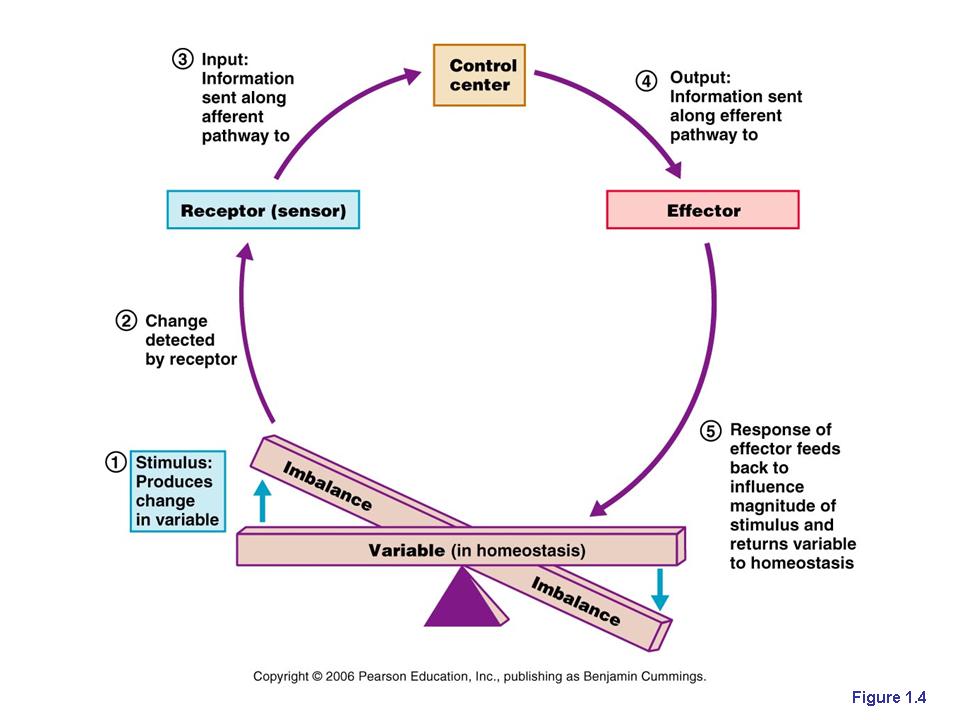

![[LS1-3] Feedback Mechanisms and Homeostasis | Biology Dictionary](https://i2.wp.com/biologydictionary.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/Homeostasis-illustration.jpg)

